Wiki Home Installation Import certificate with usb
Import certificate with usb
2026-01-13
diskless, boot, certificate, uefi, secure boot
The following explains how to import a Youngzsoft certificate from a USB drive either using the BIOS method or the MOK method (that doesn't require BIOS setup)
- Prepare an USB format in FAT32
- Download Youngzsoft v1 certificate - Used for IPXE.PXE
- Download Youngzsoft v2 certificate - Used for IPXE2025
- Download Youngzsoft v2 certificate - Used for IPXE2026 - Recommended
- Download Youngzsoft v2 certificate.esl - Used for newer motherboards that support ESL format cert only.
- Those 2 certificates (are custom certificates created by our company)
- Copy / paste the file to the USB that doesn't include anything else.
- This certificate is essential for Secure Boot access.
The BIOS way - Recommended
- In the BIOS, you can import either certificate version (V1 or V2). Both are supported, so you can choose the one that matches your setup.
- We recommend importing Youngzsoft v2 certificate in the BIOS directly with IPXE2026
- Plug in the USB on the client PC
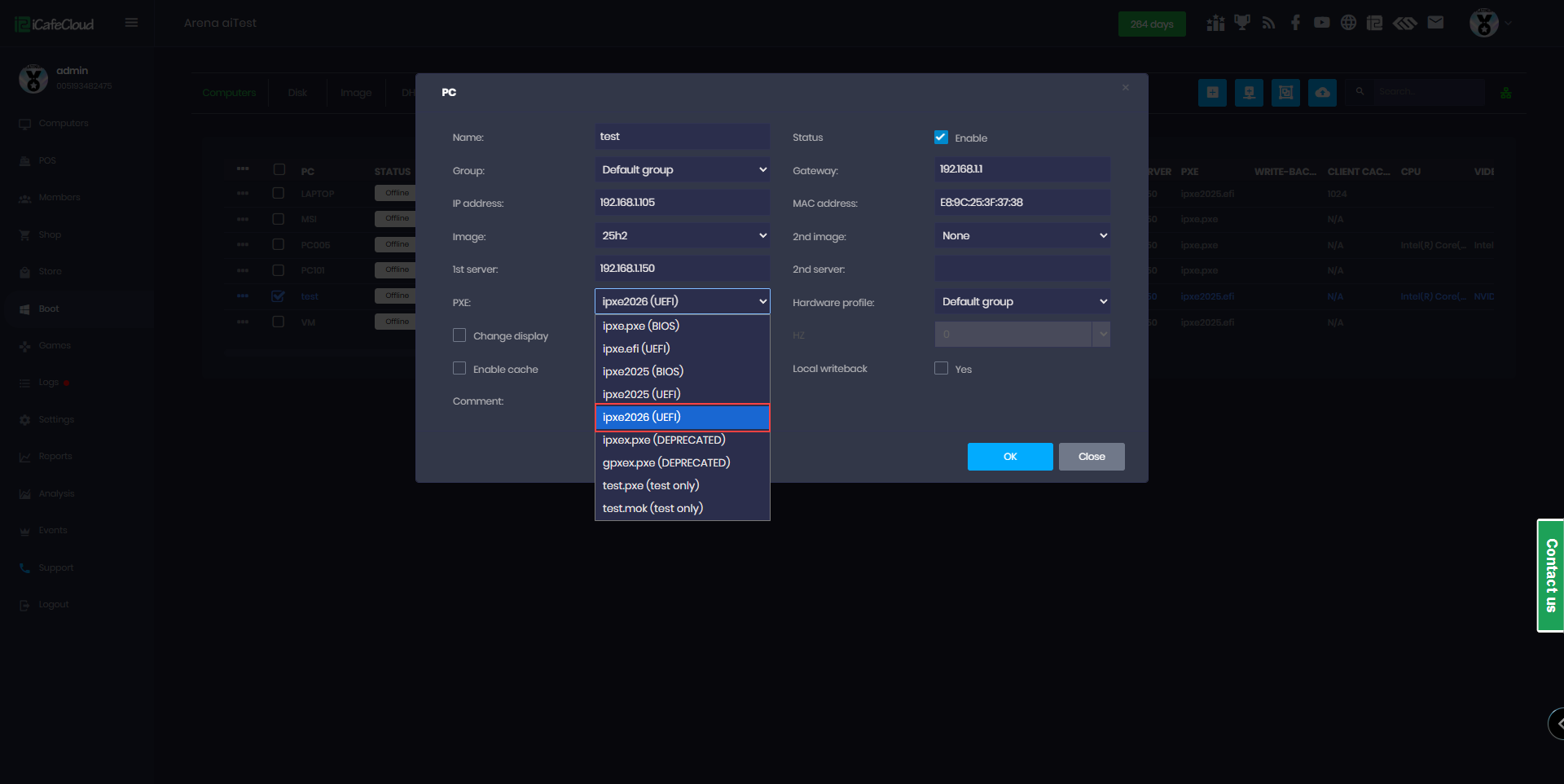
- Navigate to the Boot page, select the PC you want to boot, then click Edit. Scroll down to the PXE section and choose IPXE2026. (Figure 1)
Figure 1
The MOK way
- Youngzsoft certificate V2 imports through Mok management and works exclusively with PXE2025 as specified below
- Plug in the USB on the client PC
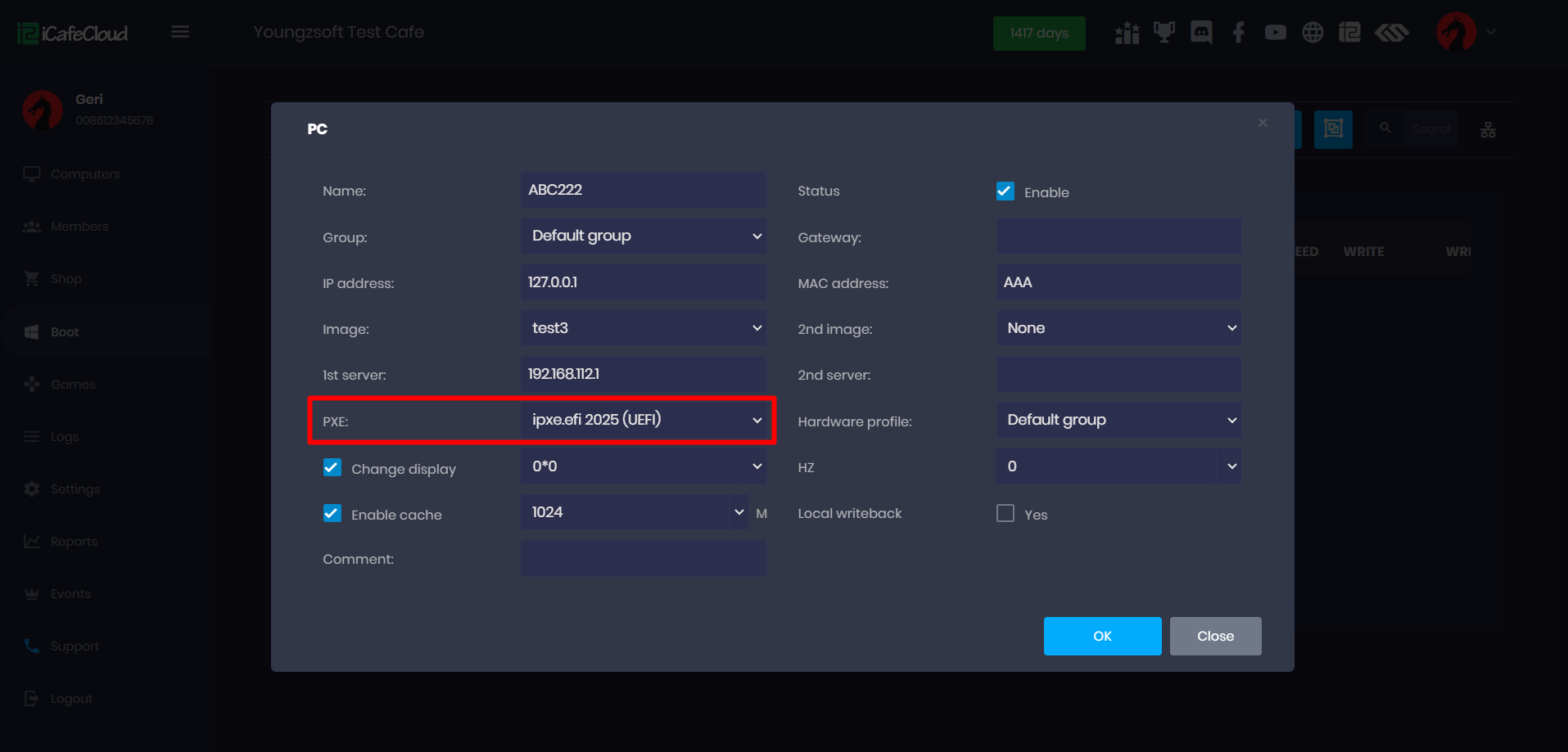
- Navigate to the Boot page, select the PC you want to boot, then click Edit. Scroll down to the PXE section and choose IPXE2025 (UEFI). (Figure 2)
Figure 1
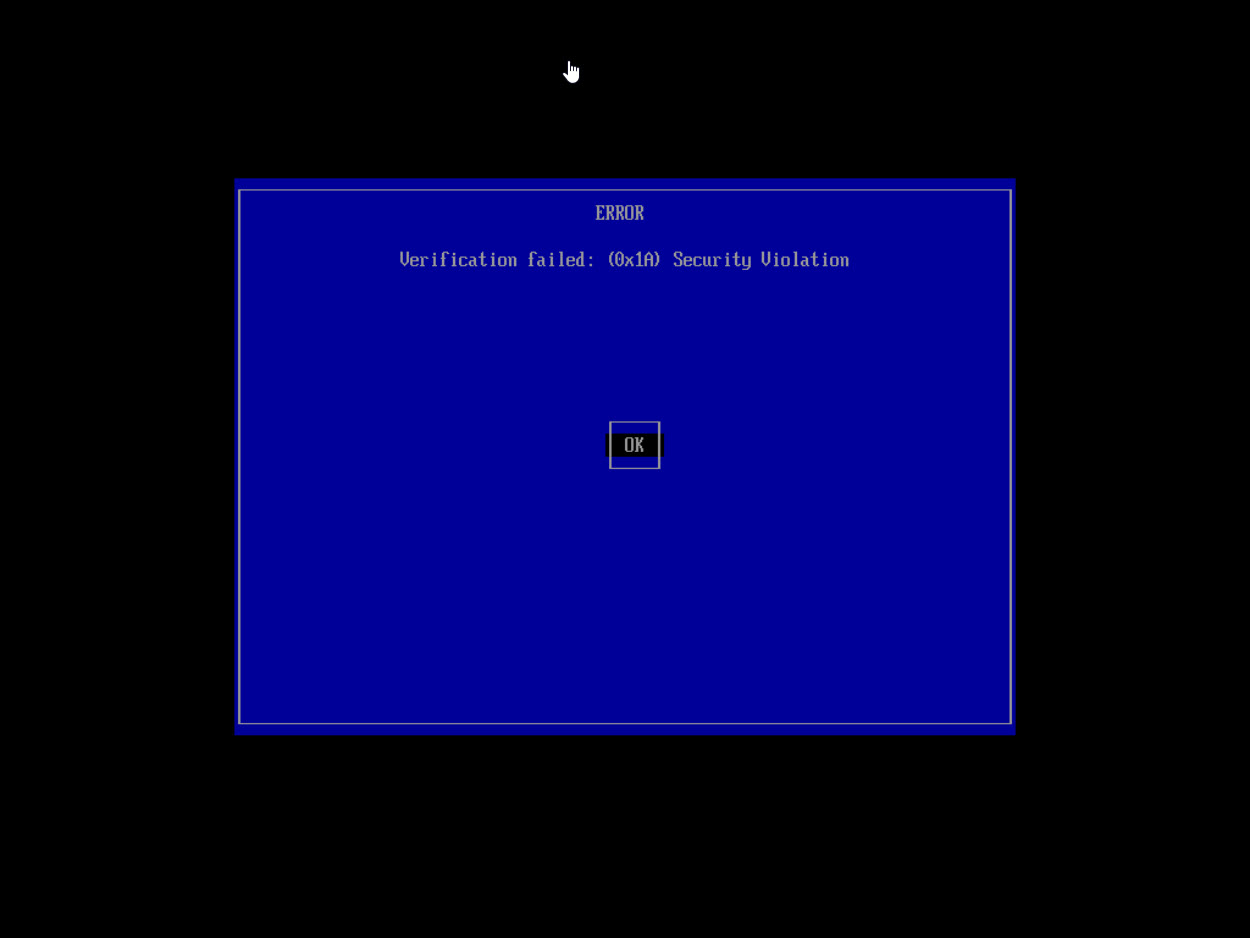
- Next, boot the PC. If Secure Boot is enabled, the PXE boot screen may display a blue screen with the error "Verification Failed: Security Violation"
- This means that the certificate has not been imported. (Figure 2)
Figure 2
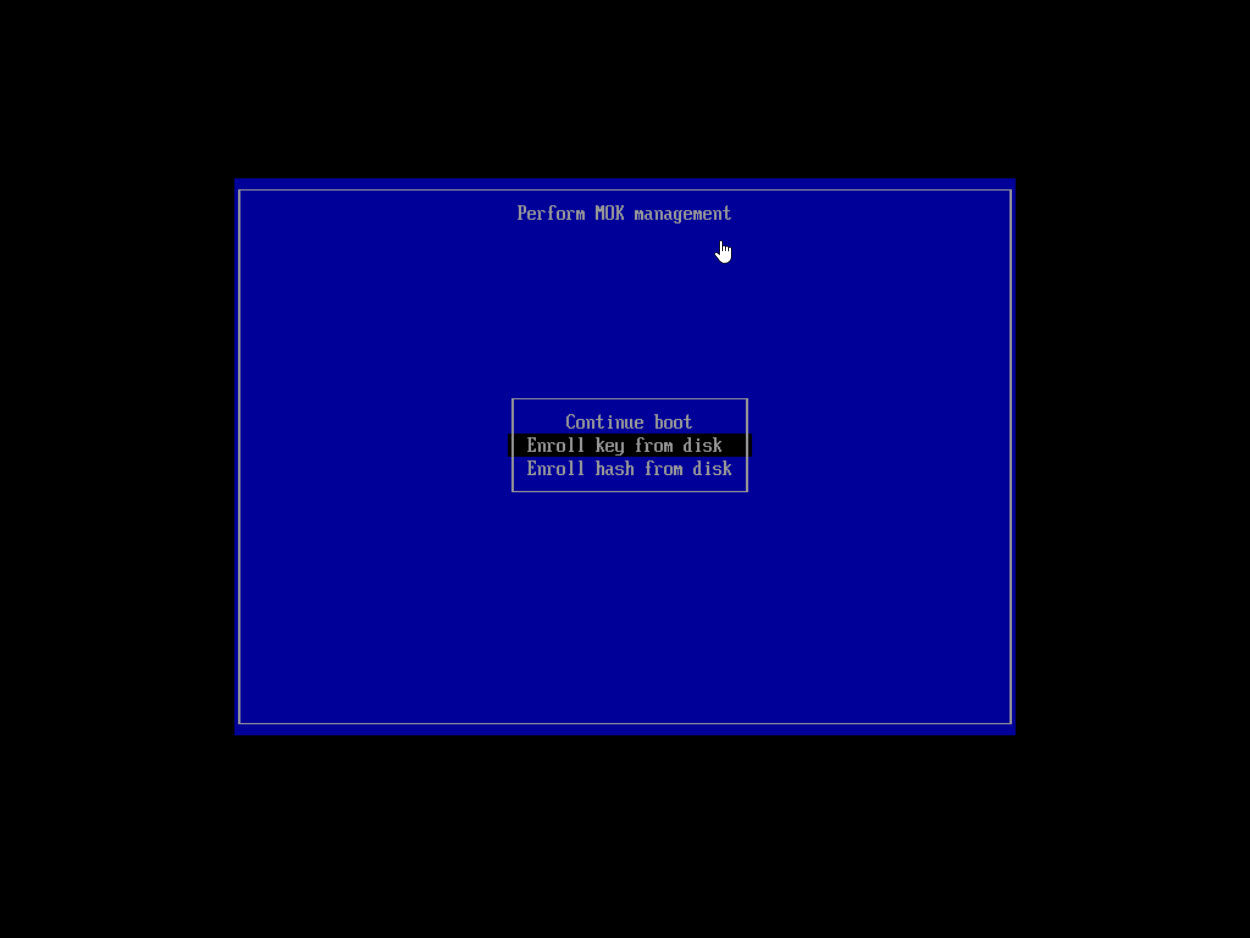
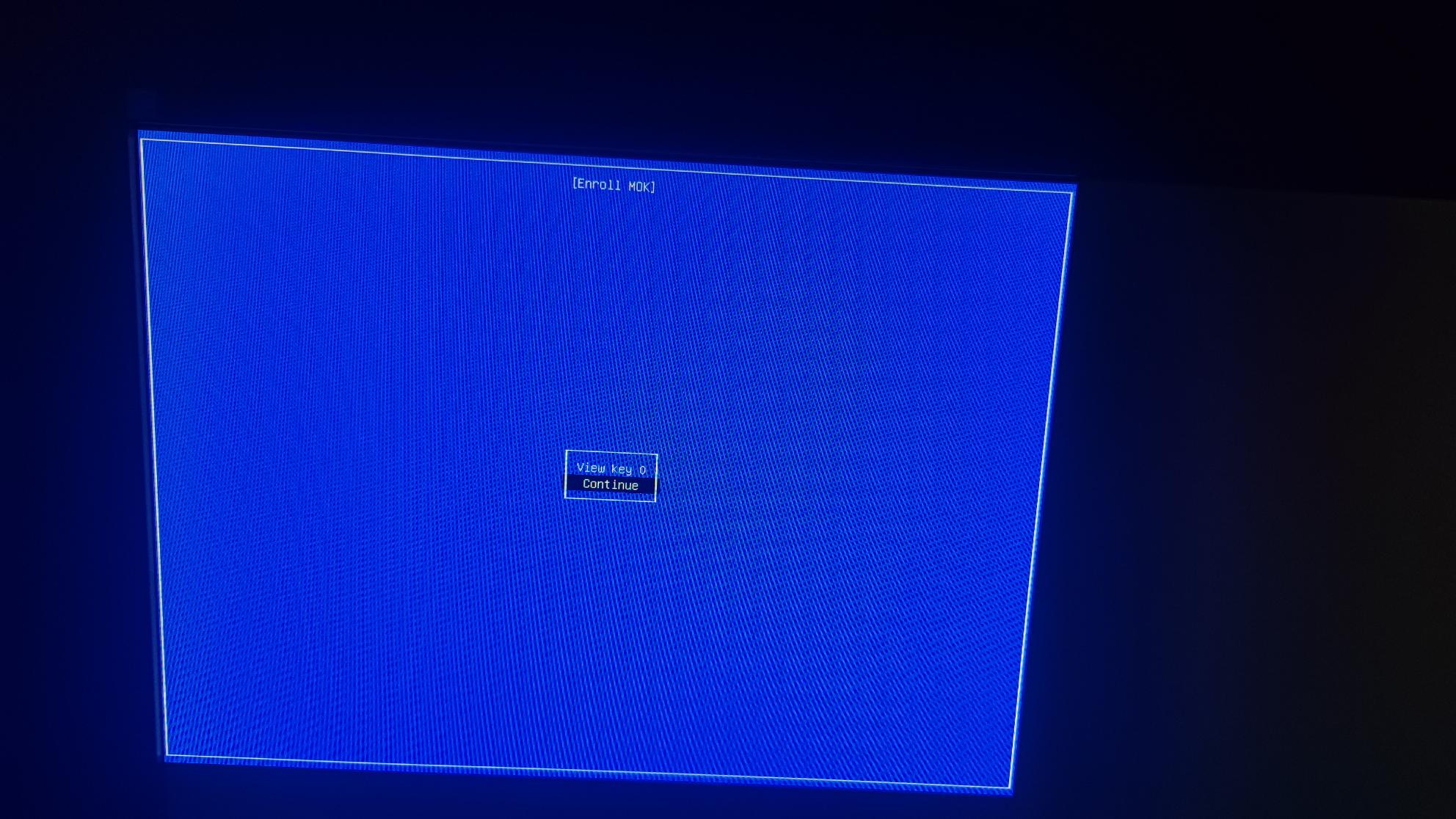
- Click OK, and the next page will appear with the MOK Management options:
Continue Boot
Enroll Key from Disk = Choose this option to import certificate from USB
Enroll Hash from Disk (Figure 3)
Figure 3
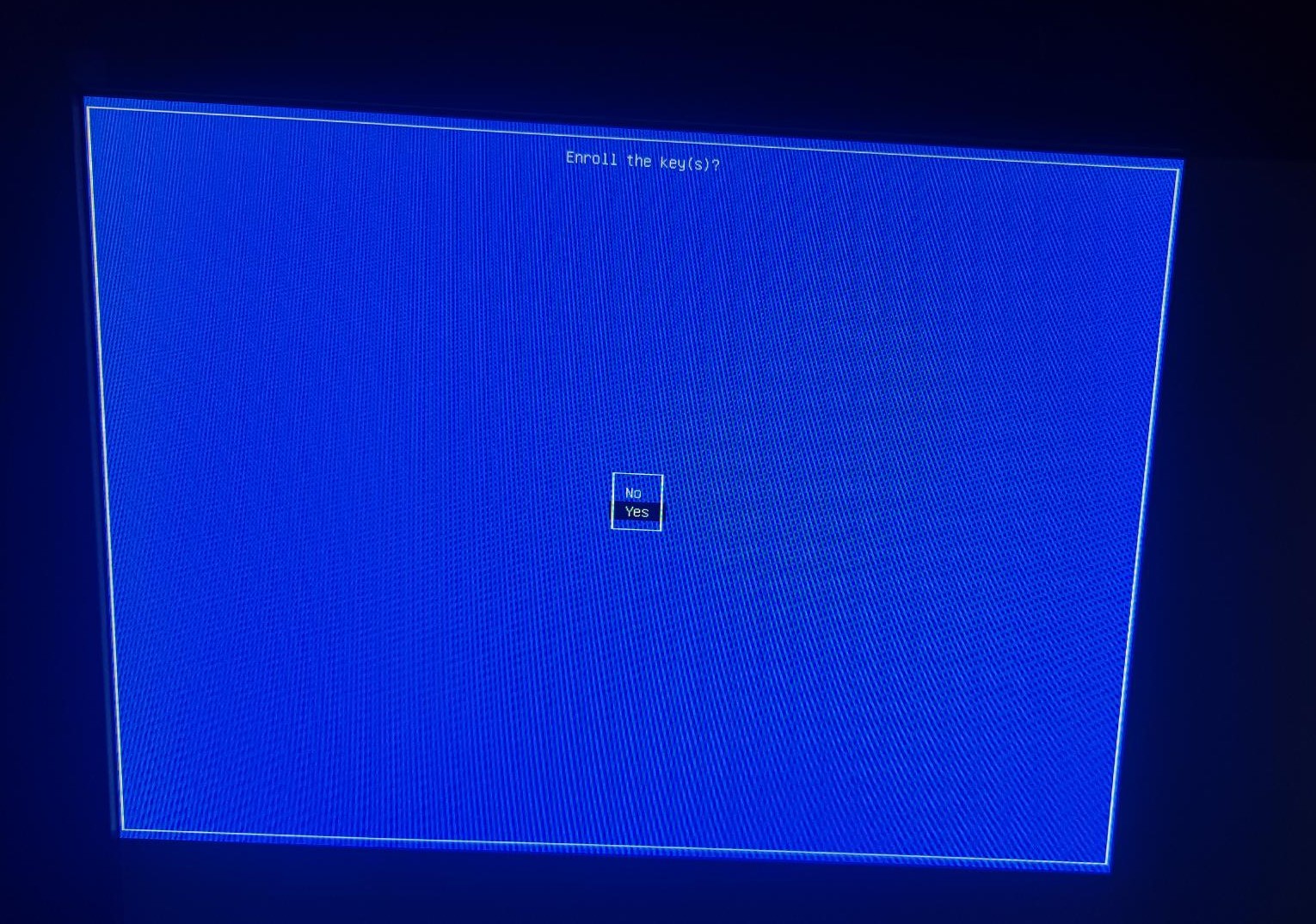
- Enroll the Keys select YES (Figure 4)
Figure 4
- Next click continue (Figure 5)
Figure 5
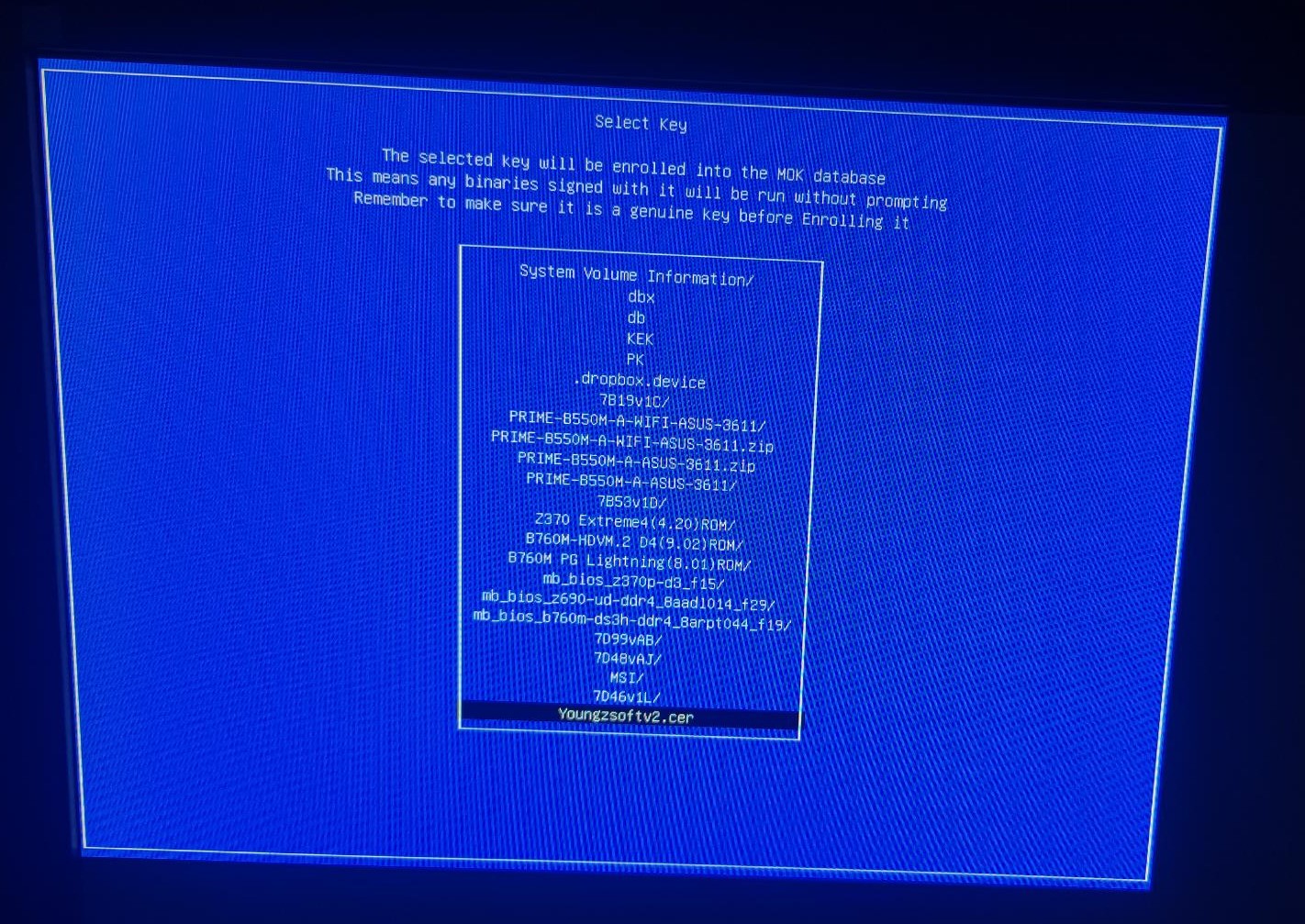
- On select keys , locate the YoungzsoftV2.cer and click on it.(Figure 6)
Figure 6
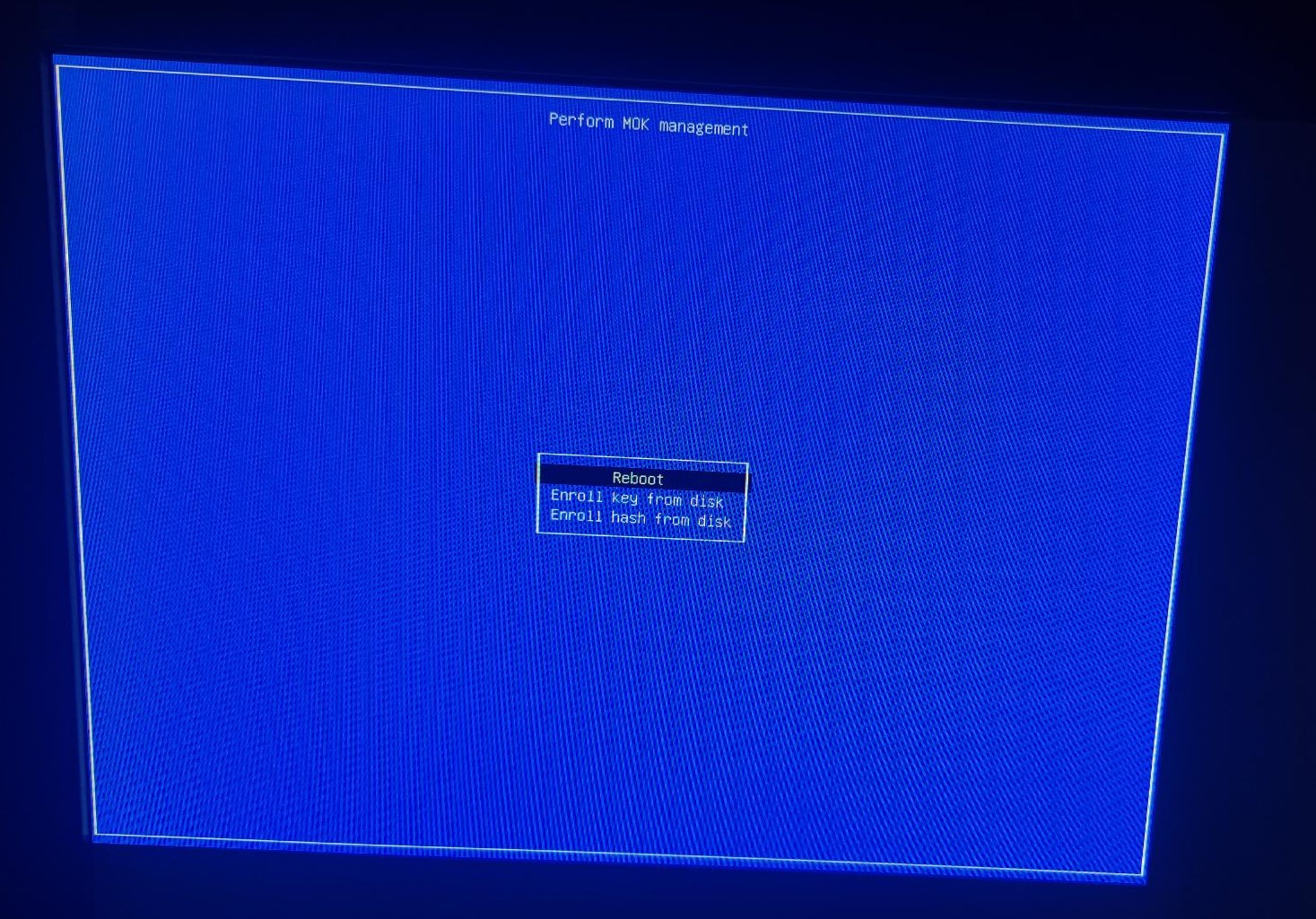
- Finally, reboot the computer. (Figure 7)
Figure 7